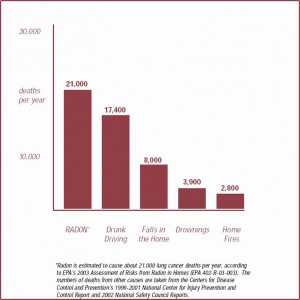
Radon is a cancer-causing, radioactive gas.

You can’t see, smell or taste it, but it may be a problem in your home. Radon is estimated to cause many thousands of deaths each year. That’s because when you breathe air containing radon, you can get lung cancer. In fact, the Surgeon General has warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States today. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, your risk of lung cancer is especially high.
Scientists are more certain about radon risks than risks from most other cancer-causing substances.
Radon gas decays into radioactive particles that can get trapped in your lungs when you breathe. As they break down further, these particles release small bursts of energy. This can damage lung tissue and lead to lung cancer over the course of your lifetime. Not everyone exposed to elevated levels of radon will develop lung cancer. And the amount of time between exposure and the onset of the disease may be many years.
Like other environmental pollutants, there is some uncertainty about the magnitude of radon health risks. However, we know more about radon risks than risks from most other cancer-causing substances. This is because estimates of radon risks are based on studies of cancer in humans (underground miners).
Smoking combined with radon is an especially serious health risk. Stop smoking and lower your radon level to reduce your lung cancer risk.
Children have been reported to have greater risk than adults of certain types of cancer from radiation, but there are currently no conclusive data on whether children are at greater risk than adults from radon.
Your chances of getting lung cancer from radon depend mostly on:
- How much radon is in your home
- The amount of time you spend in your home
- Whether you are a smoker or have ever smoked
Click here for more information on Lung Cancer in Non Smokers